Pathology & mechanisms of retinal disease
Beyond VEGF: Signaling pathways in vascular instability
DME, nAMD, and RVO are multifactorial diseases1,2–4 driven by vascular instability, characterised by vascular leakage, inflammation, and neovascularisation.5
Multiple signalling pathways, including the Ang–Tie pathway, work together to contribute to this vascular instability, and are stimulated by conditions of cellular stress.5,6
What are angiopoietins?
Angiopoietins (Ang) are a family of angiogenic growth factors, with Ang-1 and Ang-2 being best characterised for their key roles in vascular development and vascular stability.6
Ang-1 and Ang-2 bind to the Tie2 receptor and are important regulators of vascular stability.1
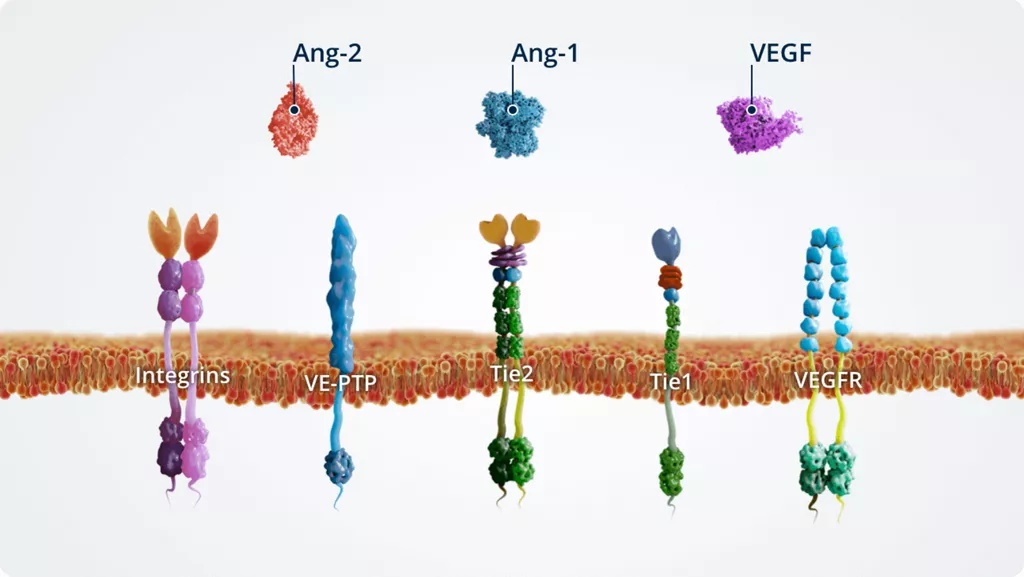
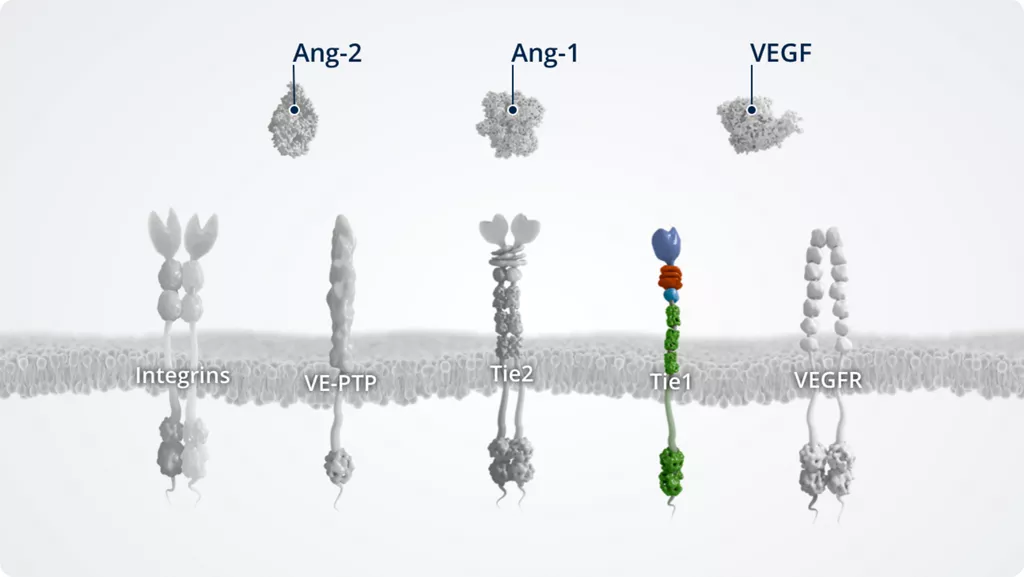
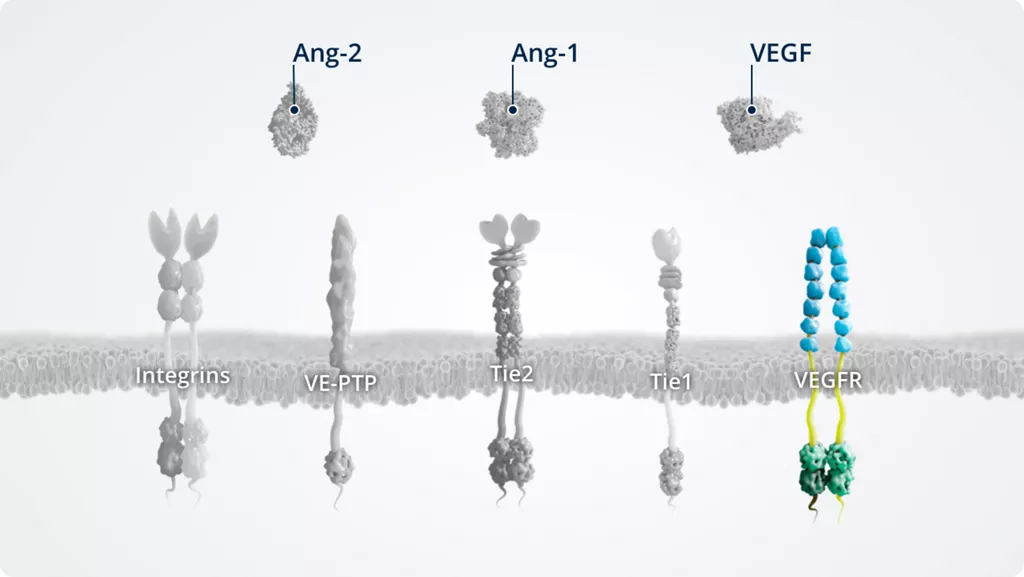
The Ang–Tie pathway
In addition to Ang-1 and Ang-2, other key players of the Ang–Tie signalling pathway include the Tie2 receptor and the Tie2 modulators Tie1 and VE-PTP.
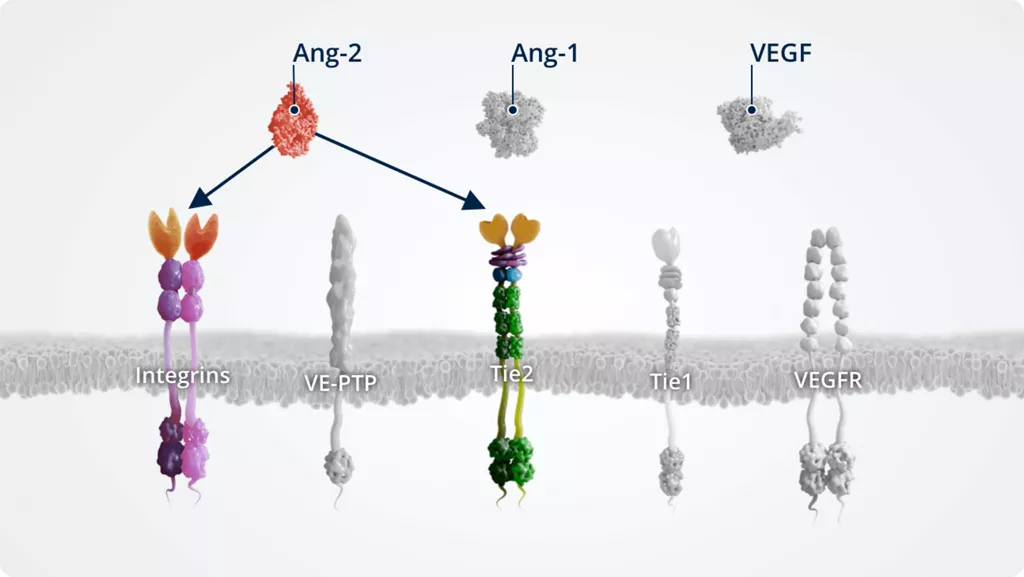
The Ang–Tie pathway also cross talks with integrins (through direct Ang-2–integrin signalling) and VEGFR, via the signalling of downstream kinases.
-
Ang-21-4
- • Angiogenic growth factor
- • Produced mainly by endothelial cells; expressed at lower levels than Ang-1 under normal conditions
- • Expression and function are context dependent:
- ◦ Tie2 antagonist under pathologic conditions
- ◦ Can also act via integrins under certain conditions
- • Levels are increased in retinal diseases (including AMD, DR, and RVO), supporting a role for Ang-2–Tie2 signalling in pathologic conditions and vascular instability.
-
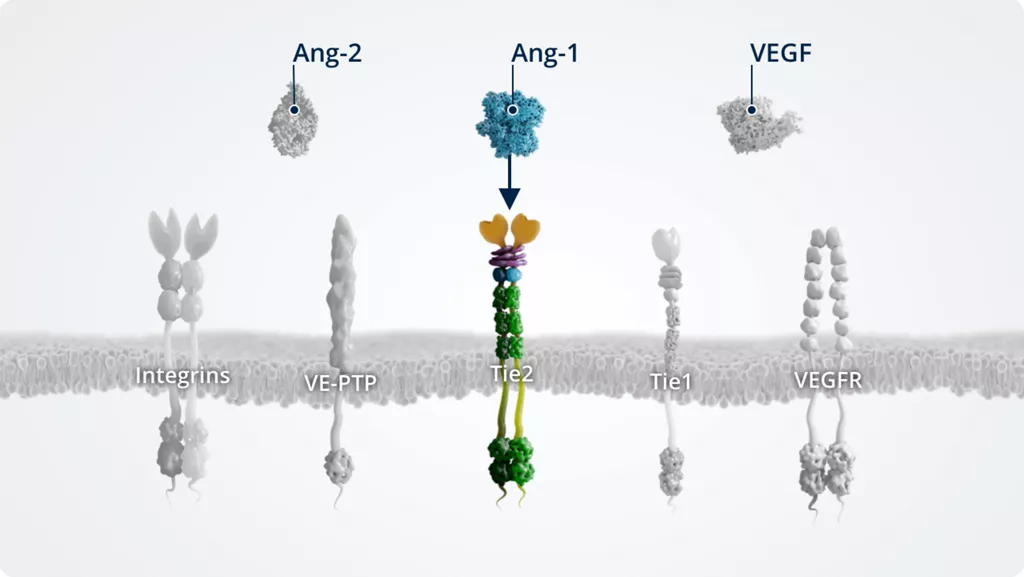
Ang-11,2
- • Angiogenic growth factor
- • Constitutively expressed by multiple cell types and maintained at high levels under normal conditions
- • Tie2 receptor agonist
- • Maintains vascular stability
-
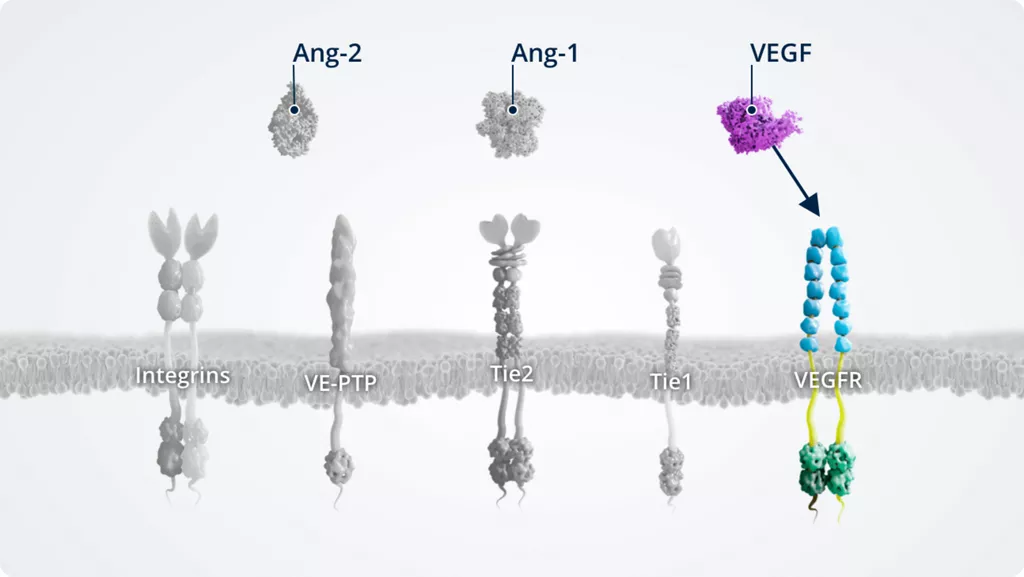
VEGF1,5,6
- • Vascular endothelial growth factor essential for angiogenesis
- • VEGFR agonist
- • Upregulated in pathologic conditions
- • Expressed by vascular endothelial cells. In addition, VEGF is also expressed on numerous non-endothelial cells, some of which include neuronal cells (e.g. astrocytes), glial cells (e.g. Müller cells), epithelial cells (e.g. retinal pigment epithelium), stromal cells, haematopoietic cells, chondrocytes, and cancer cells
-
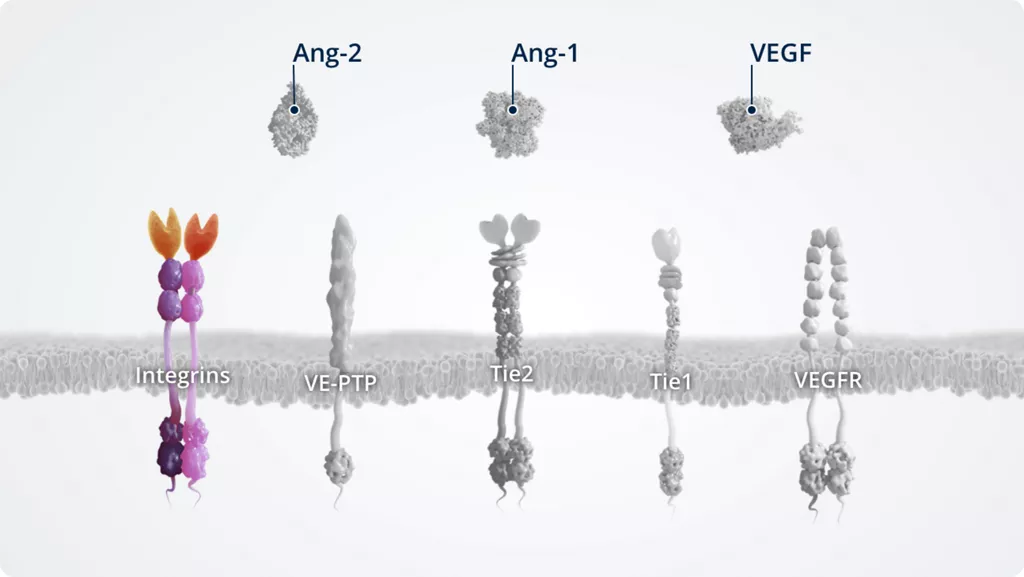
Integrins2,7
- • Transmembrane receptors that regulate cell–cell and cell–matrix adhesion as well as transmembrane signalling
- • Modulate signalling via the Ang–Tie pathway by receptor sensitisation or internalisation and degradation
- • αvβ3, αvβ5, and α5β1 integrins are receptors for Ang-2
- • Expressed on all nucleated cells of multicellular animals. This includes endothelial cells, and non-endothelial cells (e.g. fibroblasts, myocytes, glioma, and breast cancer cells)
-
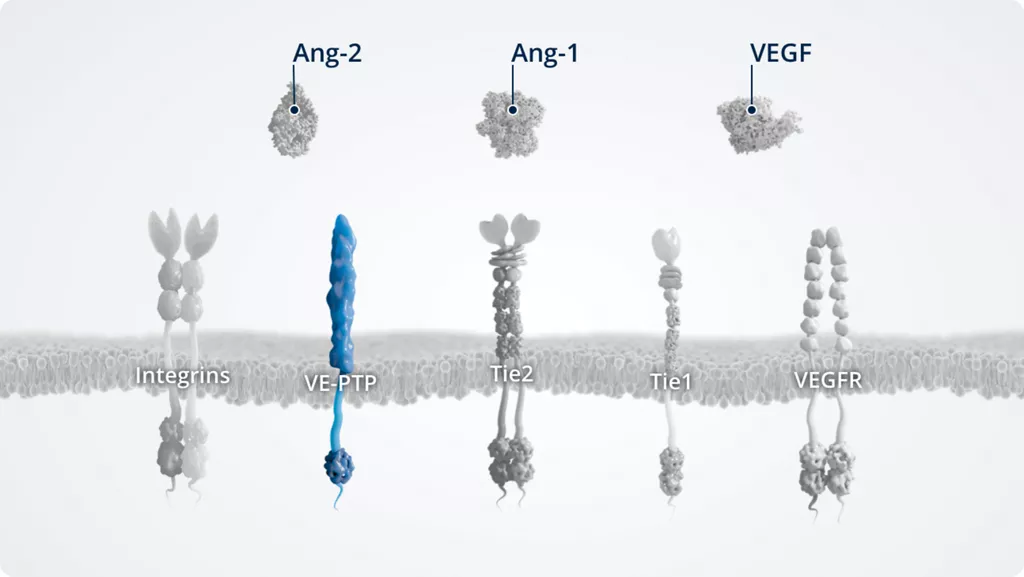
VE-PTP1,8
- • A vascular endothelial protein tyrosine phosphatase
- • Expressed by vascular (not lymphatic) endothelial cells; upregulated in hypoxic conditions
- • Negative regulator of Tie2
-
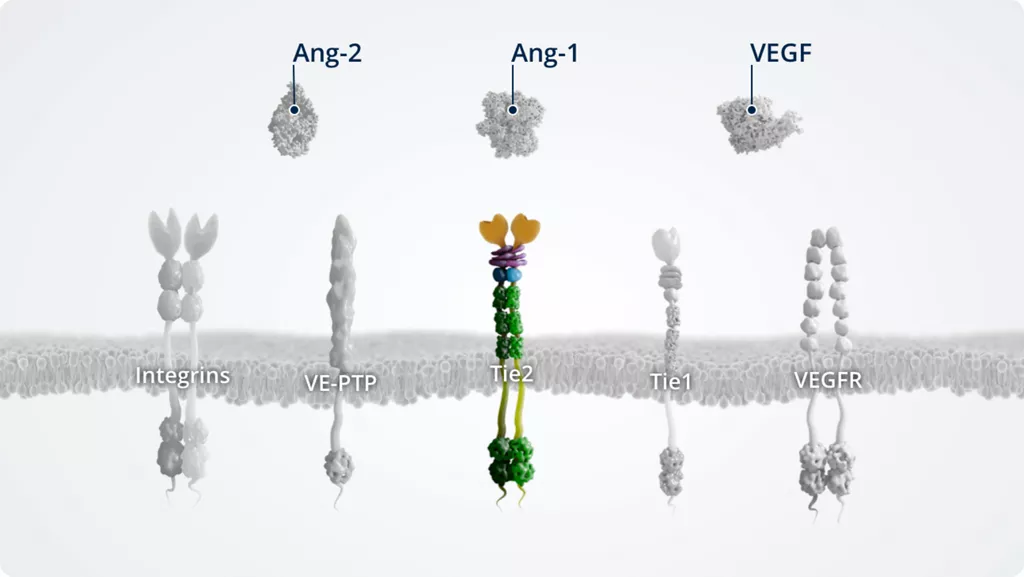
Tie21,9
- • Transmembrane tyrosine kinase
- • Constitutively active in stable blood vessels; expressed at high levels by pericytes and the blood endothelium
- • Receptor for Ang-1 and Ang-2
Mechanisms of disease
Mechanisms of disease
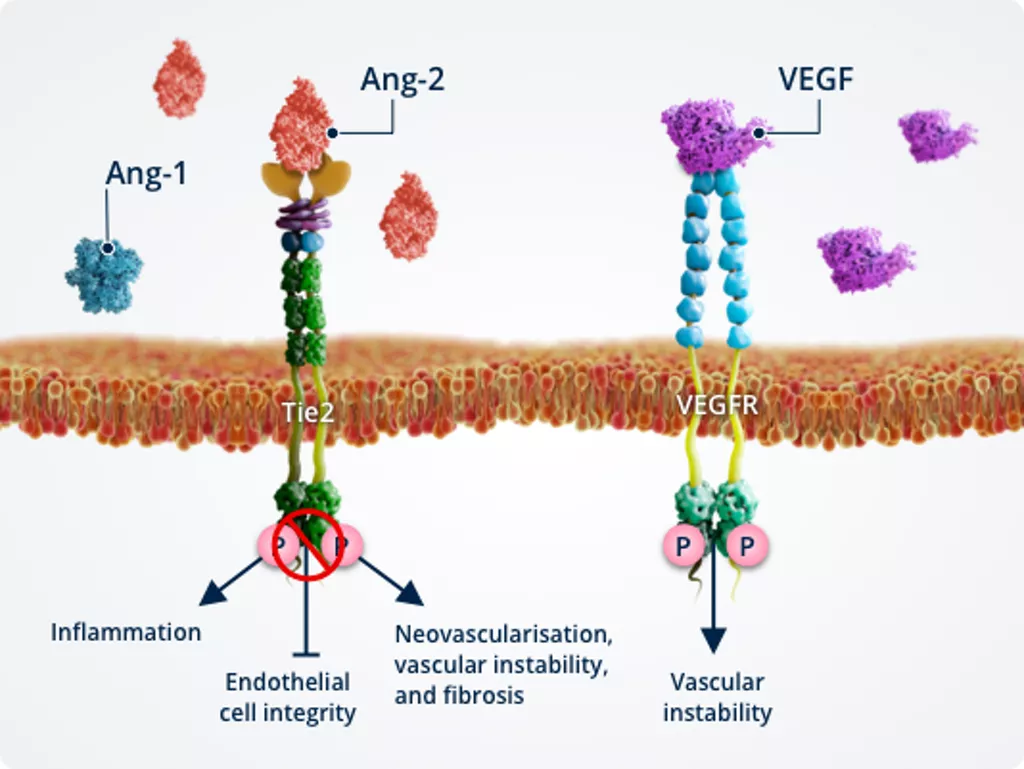
Ang-1–Tie2 signalling promotes vascular stability, maintaining homeostasis, whereas Ang-2–Tie2 signalling drives vascular instability, characterised by vascular leakage, inflammation, and neovascularisation.1,2
DME and nAMD are multifactorial diseases involving numerous signalling pathways that contribute to vascular instability.2 Watch the videos below to discover how Ang-2 and VEGF work together to drive these retinal and choroidal vascular diseases.
The role of Ang-2 and VEGF in DME
The role of Ang-2 and VEGF in nAMD
Vascular instability
Under conditions of cellular stress (i.e. in diseases such as DME, nAMD, and RVO), an angiogenic switch leads to elevated levels of Ang-2 and VEGF, potentiating angiogenic and inflammatory signals.6


Vascular leakage and neovascularisation1-5
Elevated Ang-2 levels inhibit Tie2, which:
- Primes blood vessels for angiogenesis (pericyte dropout and apoptosis)
- Reduces integrity of endothelial cell junctions, which contributes to vascular leakage
- Amplifies the effects of VEGF on blood vessels
Elevated VEGF levels:
- Promote neovascularisation
- Lead to further vascular leakage

Inflammation5
Inhibition of Tie2 by Ang-2 also modulates immune signalling, leading to:
- Leukocyte adhesion to the vessel walls and transmigration into the surrounding tissues
- Release of pro-inflammatory and pro-angiogenic cytokines
- Sensitisation of blood vessels to the effects of cytokines and amplification of those effects
See how Ang-2 drives vascular instability in retinal and choroidal vascular disease
See a detailed illustration showing how Ang-1 and Ang-2 regulate vascular stability and instability
Downstream effects of Ang-Tie signalling
Both Ang-1 and Ang-2 bind to Tie2, with different effects on the downstream signalling pathways.1,2
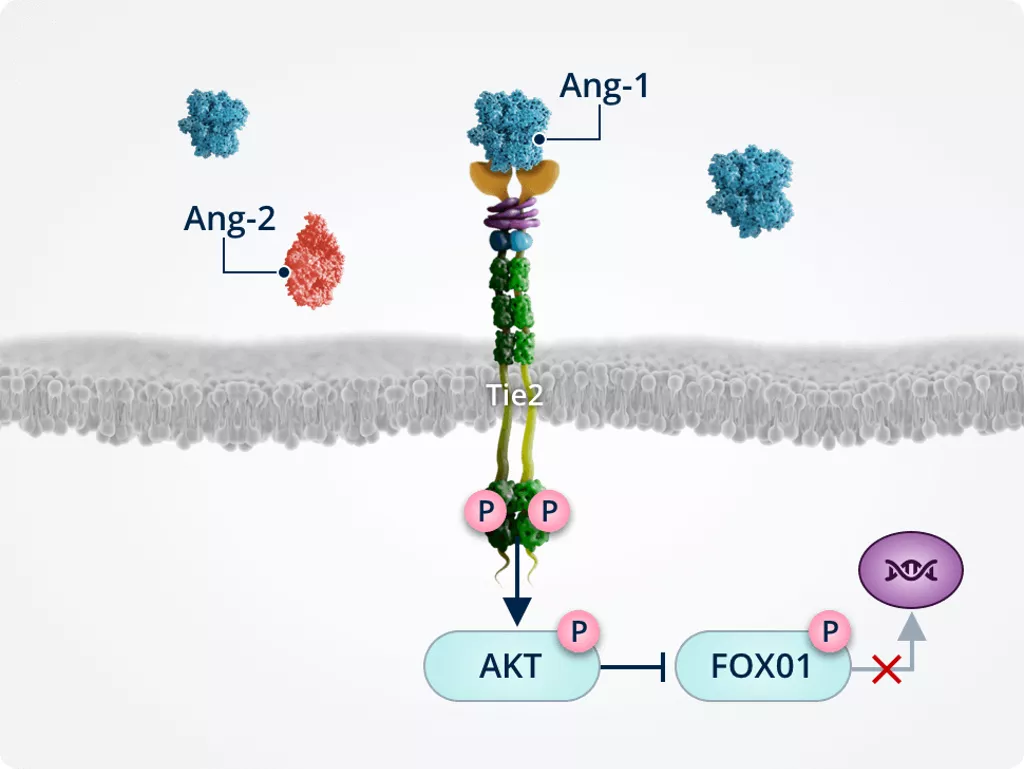
Ang-1–Tie2 signalling
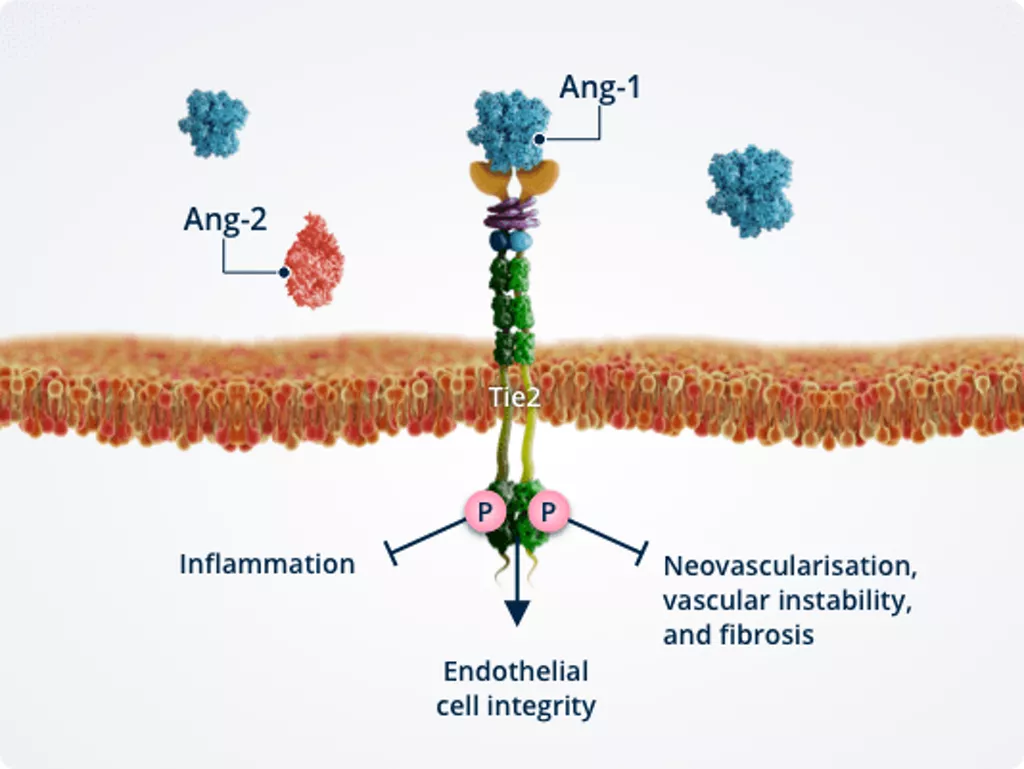
Healthy vasculature1,2,6,7
In healthy vasculature, Ang-1–Tie2 signalling actively maintains vascular homeostasis and serves as an important molecular brake against vascular instability.
Activated Tie2 promotes endothelial cell integrity, thereby ensuring vascular stability.
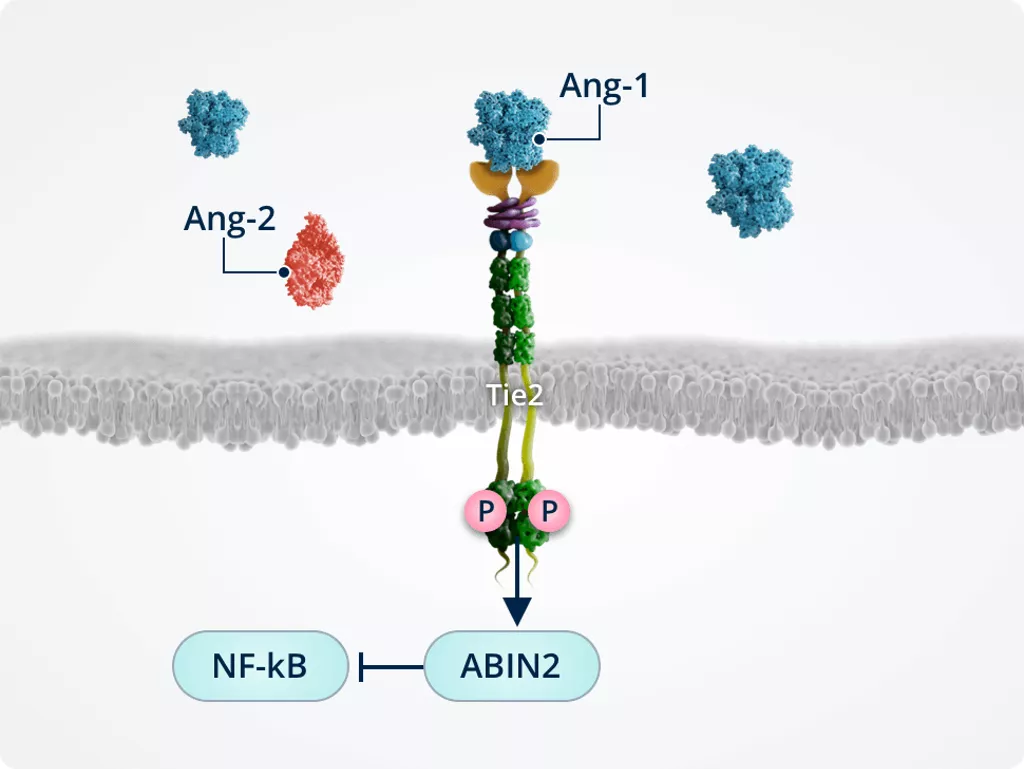
Inhibiting inflammation1,2,6
Tie2-mediated activation of ABIN2 protects endothelial cells by inactivating the transcription factor NF-κB, which is a key transcriptional regulator of inflammatory responses in endothelial cells and transmigration into the surrounding tissues.
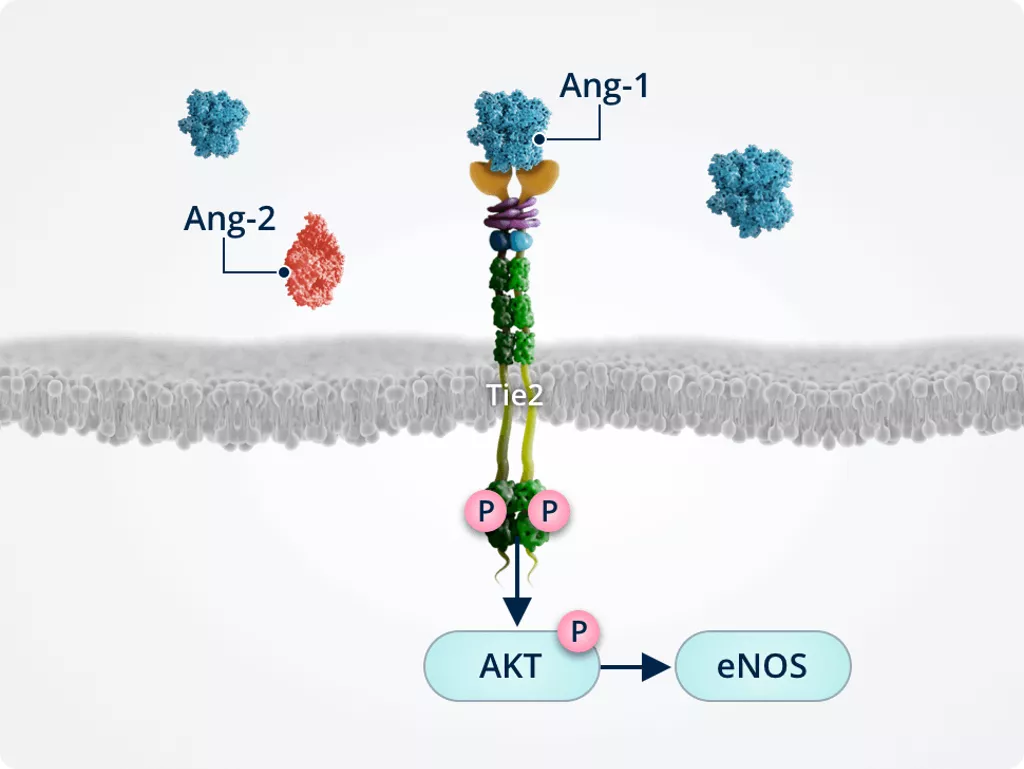
Endothelial cell integrity1,2,6
Ang-1–induced Tie2 phosphorylation results in the activation of AKT. AKT signalling activates survival promoting pathways such as eNOS.
Inhibiting neovascularisation, vascular leakage and fibrosis1,2,6,7
Ang-1–induced Tie2 phosphorylation triggers AKT activation/phosphorylation; activated AKT phosphorylates and inactivates FOXO1, preventing its translocation to the nucleus and reducing expression of its target genes:
- Ang-2
- Genes involved in:
- Vascular remodelling and instability
- Endothelial cell apoptosis
- Fibrosis
Ang-2–Tie2 signalling
Pathway cross-talk1,2,6,7
Inhibition of Tie2 by Ang-2 amplifies the vascular leakage and neovascularisation effects of VEGF, and has other VEGF-independent effects.
Together, Ang-2 and VEGF act in synergy to promote vascular instability.
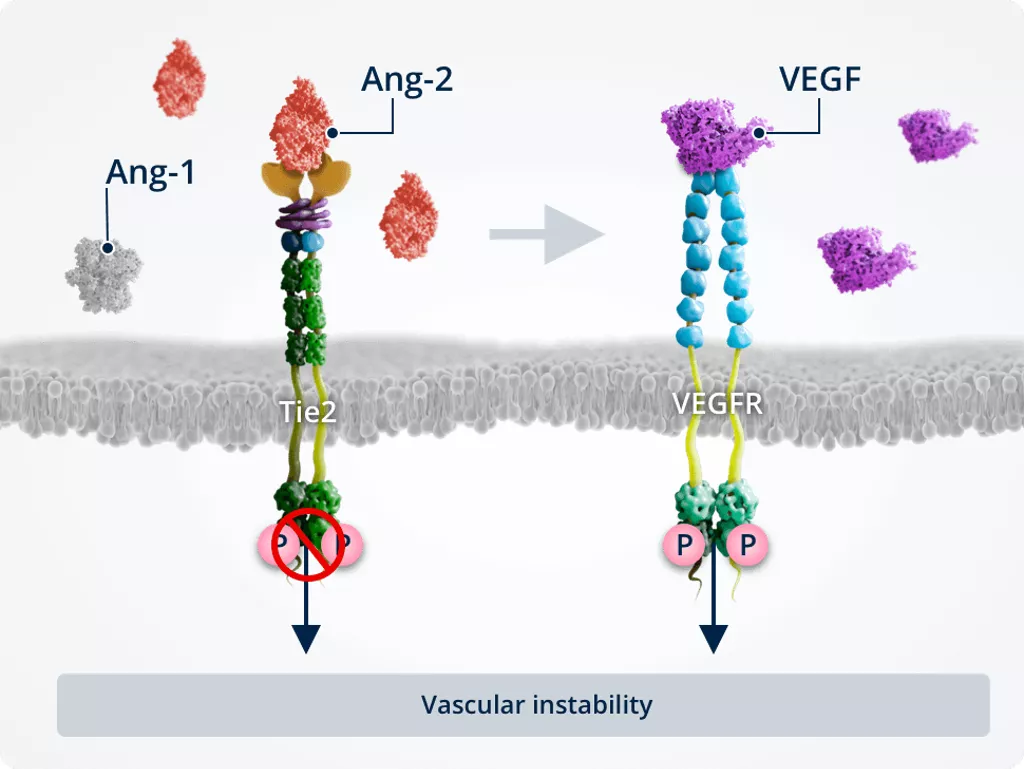
Vascular instability1,2,6,7
In pathologic conditions, Ang-2–Tie2 binding inhibits Tie2, allowing activation of the FOXO1 pathway. This results in inhibition of survival signalling and promotion of vascular instability..
Ang-2 also cross-talks with the VEGF signalling pathway, amplifying vascular leakage and neovascularisation to further promote vascular instability.
Inflammation1,2,6
Ang-2 prevents the Tie2-mediated activation of ABIN2, which in turn does not inactivate NF-kB. NF-kB drives expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and adhesion molecules (i.e. ICAM1 and VCAM1) and primes the endothelium for TNF-α–induced leukocyte adhesion and transmigration into the surrounding tissues.
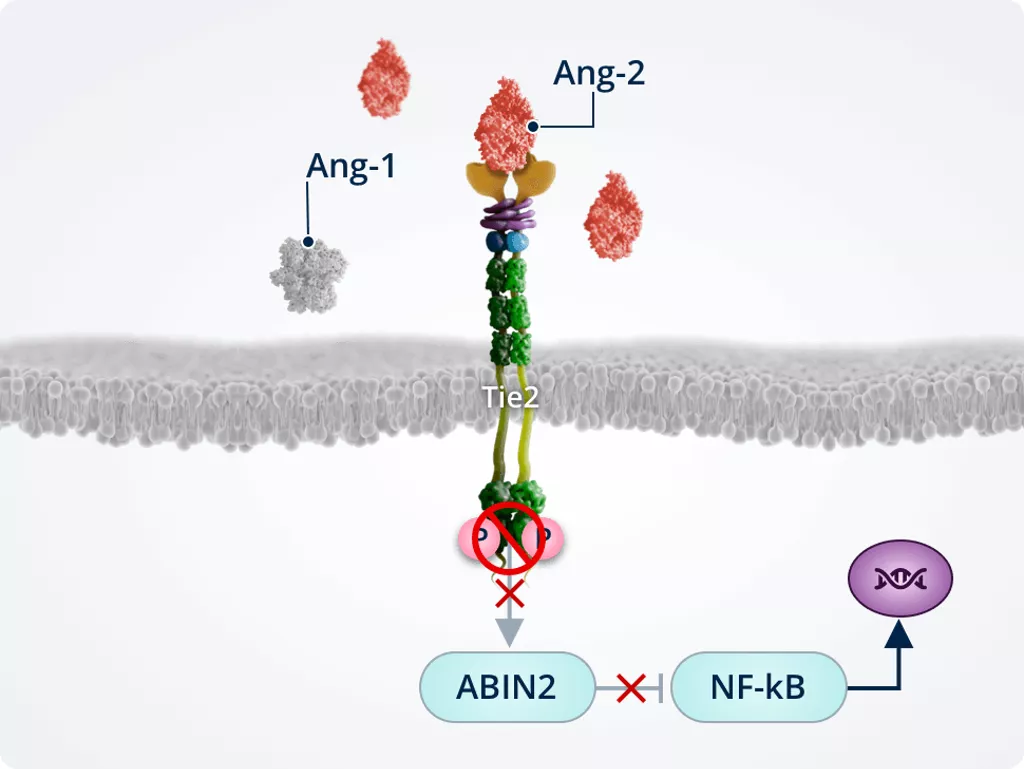
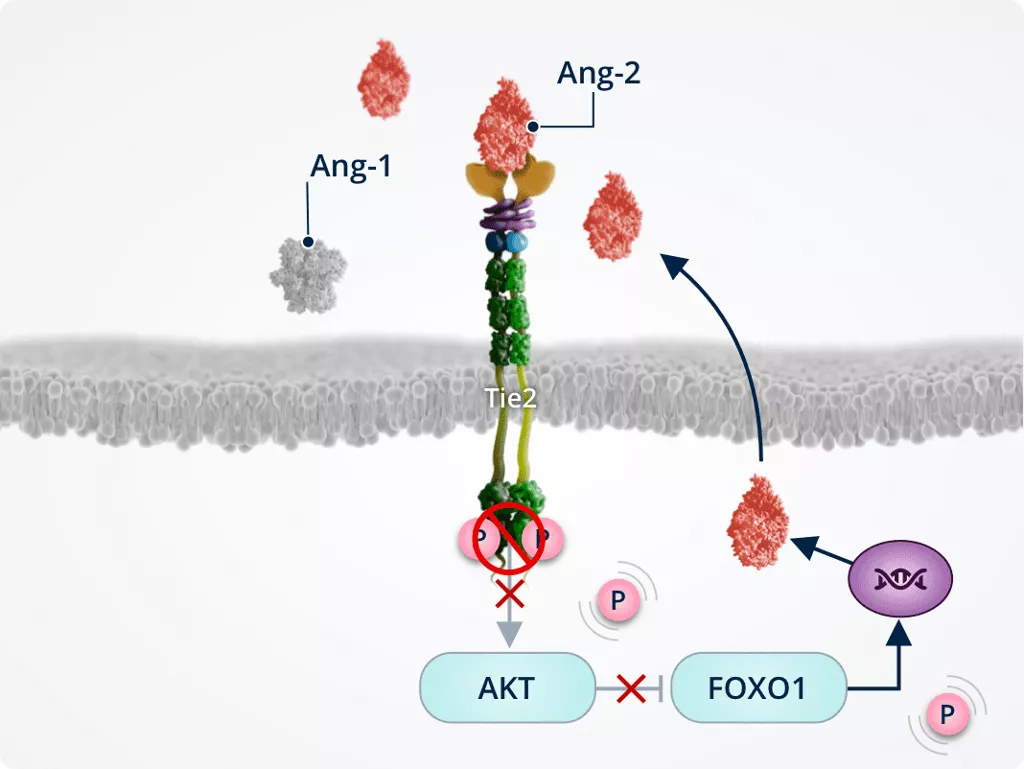
Promoting neovascularisation, vascular leakage, and fibrosis1,2,6,7
Tie2 inhibition by Ang-2 inactivates AKT; inactivated AKT dephosphorylates and activates FOXO1, which translocates to the nucleus and increases expression of its target genes:
- Ang-2
- Genes involved in:
- Vascular remodelling and instability
- Endothelial cell apoptosis
- Fibrosis
FOXO1 nuclear translocation and upregulation of Ang-2 expression leads to a positive feedback loop of Ang-2 production and Tie2 inhibition.
Context-dependent effects of Ang-2 signalling
The effects of Ang-2 signalling on endothelial cells are context-dependent and mediated by several factors, including expression of receptors and modulators and levels of ligands.1,2,8–13
Role of VEGF concentration in Ang-2–Tie2 signalling8
The effects of Ang-2–Tie2 signalling differ depending on the presence or absence of VEGF, resulting in the promotion of endothelial cell integrity or angiogenesis and vascular instability.
Low levels of VEGF
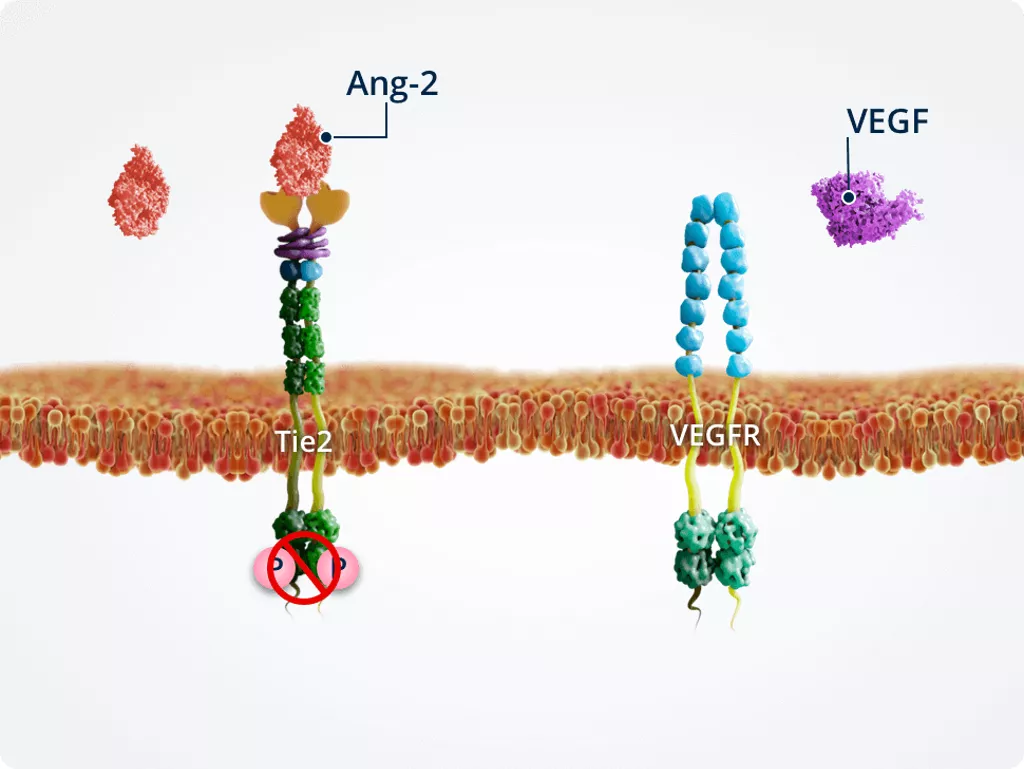
Endothelial cell integrity
VEGF is essential for endothelial cell integrity. When VEGF is suppressed under experimental conditions, Ang-2–Tie2 signalling promotes endothelial cell death and vessel regression.
High levels of VEGF
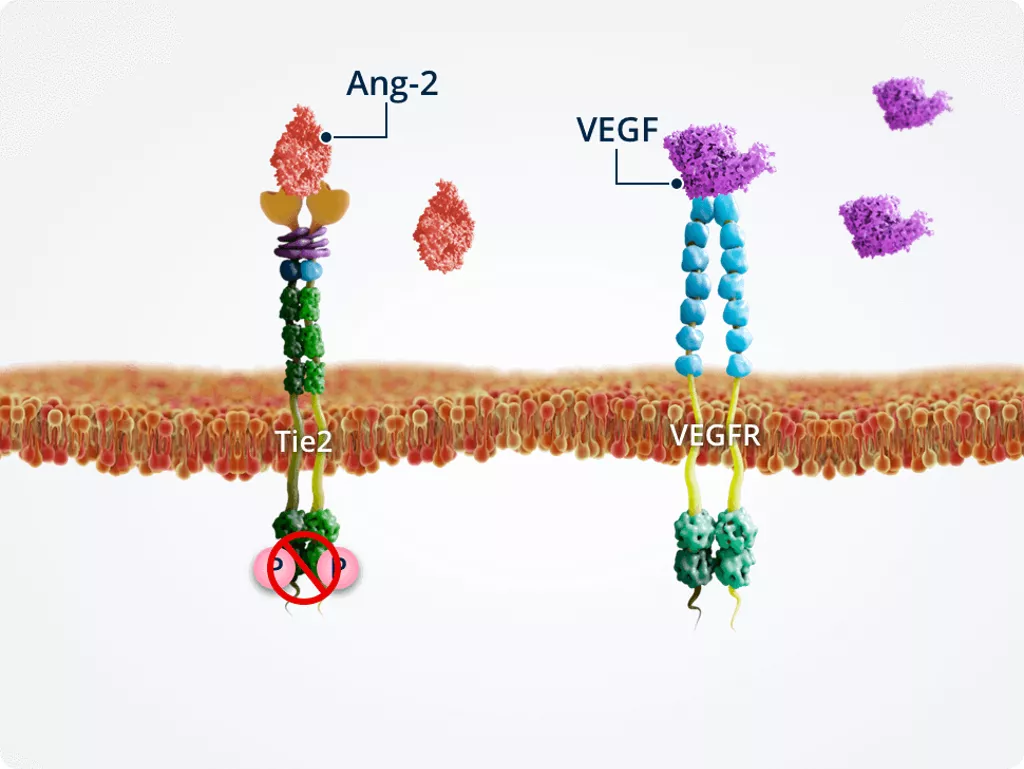
Vascular instability
Under pathologic conditions in which Ang-2 and VEGF are upregulated, high levels of VEGF modulate the effects of Ang-2. Therefore, Ang-2 and VEGF act synergistically to promote vascular instability and angiogenesis.
Ang-2 signalling via integrins inendothelial cells2,9,10
The expression levels of Tie2 versus integrin receptors in endothelial cells impact the effects of Ang-2 signalling via the phosphorylation status of FAK, an integrin adaptor protein associated with barrier function.
Absence of Tie2
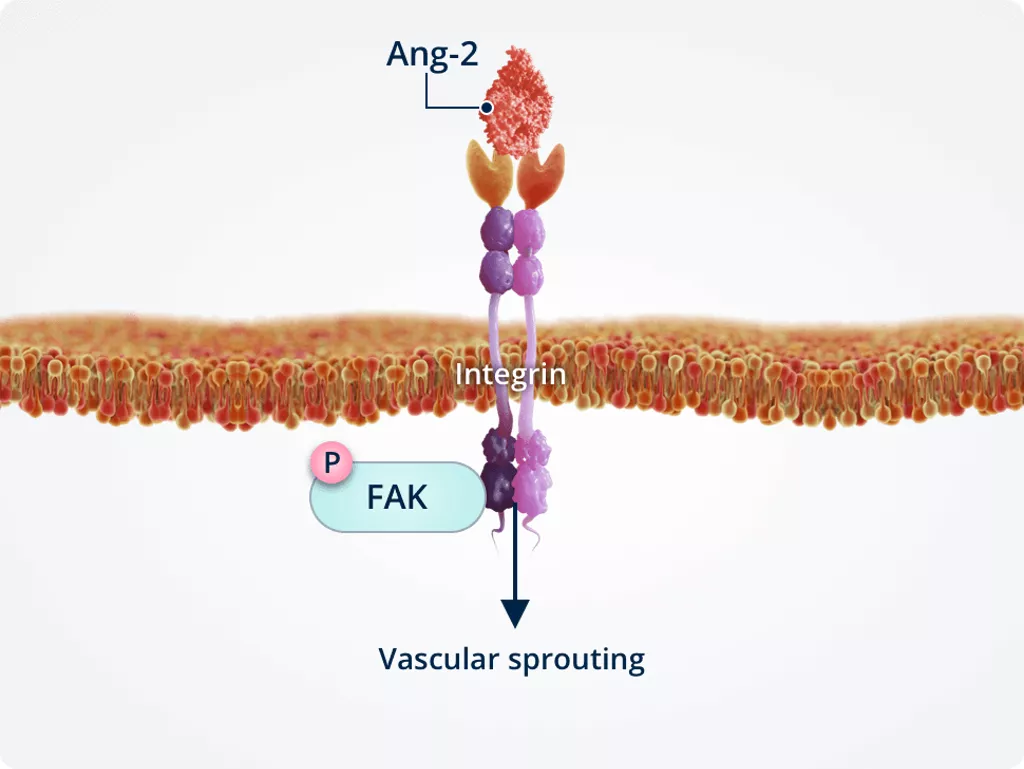
Vascular sprouting
In the absence of Tie2, Ang-2 directly binds integrins. This stimulates endothelial cell migration and vascular sprouting.
Presence of Tie2
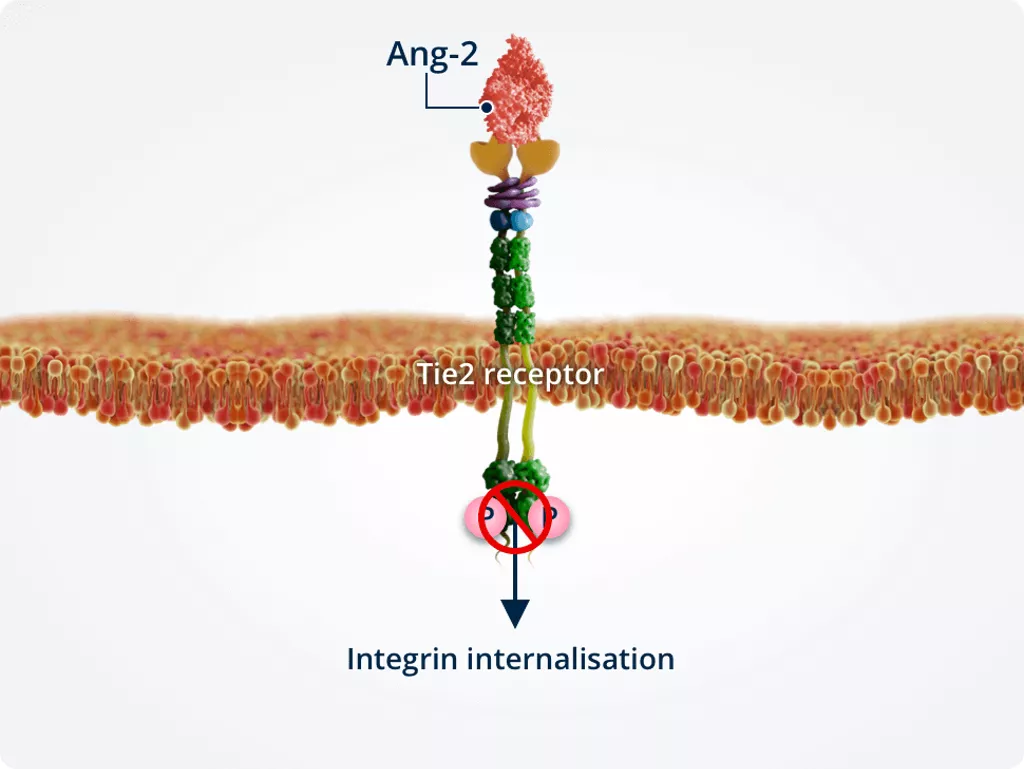
Vascular sprouting
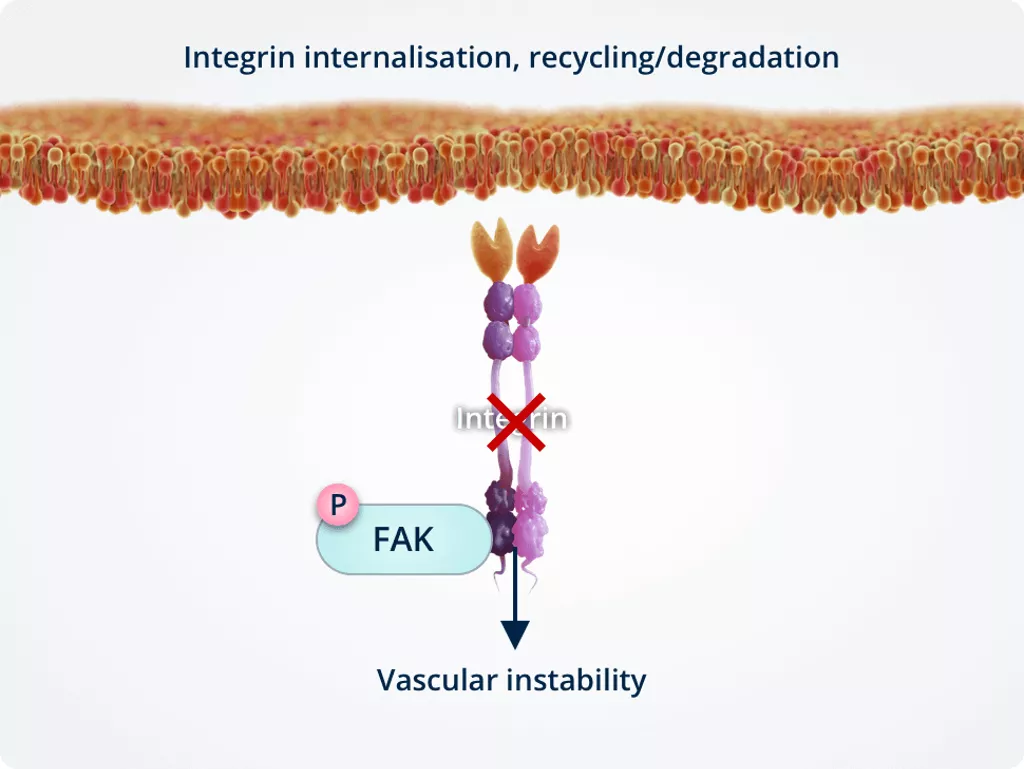
In the presence of Tie2, Ang-2 binds Tie2 directly, stimulating integrin internalisation.
Internalised integrins are processed in intracellular compartments and targeted for either recycling or degradation. This results in vascular instability.
Role of Tie1 in Ang-2–Tie2 signalling2,11,12
Tie1 acts as a modulator of Tie2, and its expression impacts the role of Ang-2 in Ang-2–Tie2 signalling.
Homeostatic conditions
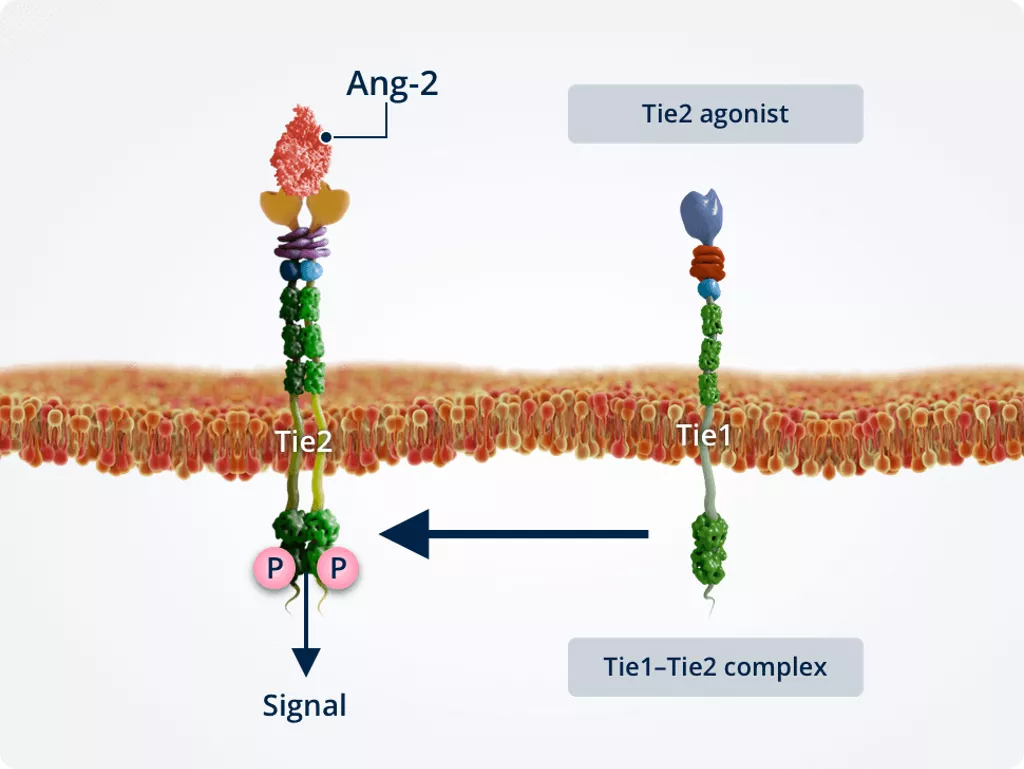
Normal conditions
Under normal conditions, Tie1 and Tie2 form a complex, promoting the Tie2 agonist function of Ang-2. This activates Tie2 and leads to the same downstream signalling effects as Ang-1–Tie2 signalling.
Inflammatory conditions
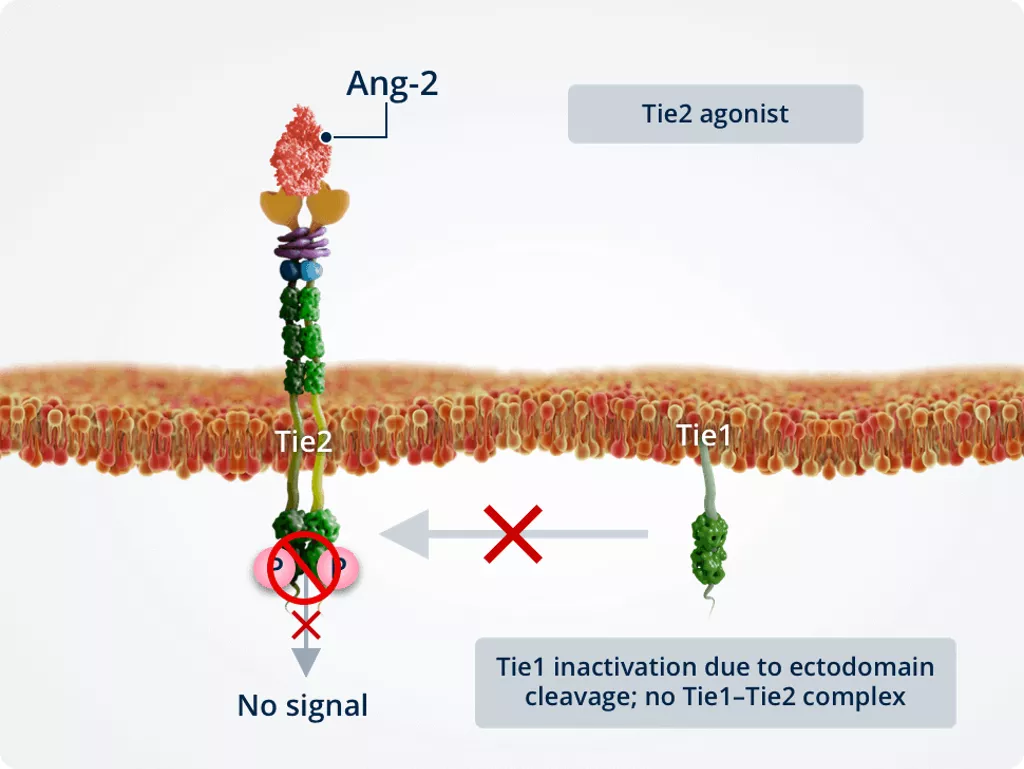
Inflammatory conditions
Under inflammatory conditions, Tie1 is inactivated owing to ectodomain cleavage, preventing the formation of a Tie1–Tie2 complex. Inactivation of Tie1 promotes the Tie2 antagonist function of Ang-2.
Role of VE-PTP in Ang-2–Tie2 signalling2,13
VE-PTP acts as a modulator of Tie2, and its expression impacts the role of Ang-2 in Ang-2–Tie2 signalling.
Absence of VE-PTP
Ang-2 acts as a Tie2 agonist

Tie2 responsiveness
VE-PTP sets the threshold for Tie2 responsiveness to Ang-1 and Ang-2. In the absence of VE-PTP (such as in lymphatic endothelial cells, where it is not expressed), Ang-2 acts as a Tie2 agonist, leading to Tie2 activation.
Presence of VE-PTP
Ang-2 acts as a Tie2 antagonist

Tie2 affinity
In the presence of VE-PTP (such as in vascular endothelial cells, where it is highly expressed), Ang-2 has low affinity for Tie2 and acts as a Tie2 antagonist, leading to inhibition of Tie2.
References
- Saharinen P, et al. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2017;16:635–61
- Joussen AM, et al. Eye. 2021;35:1305–16
- Klaassen I, et al. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2013;34:19–48
- Bolinger MT, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17:1498
- Fiedler U, Augustin HG. Trends Immunol. 2006;27:552–8
- Augustin HG, et al. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2009;10:165–77
- Akwii RG, et al. Cell. 2019;8:E471
- Lobov IB, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99:11205–10
- Felcht M, et al. J Clin Invest. 2012;122:1991–2005
- Thomas M, et al. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:23842–9
- Korhonen EA, et al. J Clin Invest. 2016;126:3495–510
- Kim M, et al. J Clin Invest. 2016;126:3511–25
- Souma T, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018;115:1298–303